check_sap_health
Description
check_sap_health is a plugin designed to monitor SAP NetWeaver instances. It was developed as an easily extensible tool to monitor both technical parameters from the CCMS (Computing Center Management System) as well as business-related facts via RFC/BAPI.
The plugin communicates either with a Solution Manager or directly with application servers. Monitoring of SAP load balancing is also possible by connecting to the message server of a central instance.
With check_sap_health it is possible to monitor:
- CCMS metrics (using SAP’s own thresholds or defining custom thresholds)
- Background jobs (duration as well as exit status)
- Short dumps and failed updates
- Process counts and workload analysis
- IDoc status verification
A highlight of this plugin is its simple API which allows users to write small extensions to monitor individual business logic using the RFC/BAPI interface.
Installation
The plugin requires the SAP NetWeaver RFC SDK and the Perl module sapnwrfc. In OMD, the plugin is already included; only the SDK and its dependencies need to be installed separately.
Prerequisites
- SAP NetWeaver RFC SDK: Download from SAP Service Marketplace
- SAP Cryptographic Library: Required for SNC (Secure Network Communication)
- Perl module sapnwrfc: Available from https://github.com/lausser/perl-sapnwrfc
Installation Steps
- Download the NW RFC SDK from SAP
- Extract using SAPCAR tool
- Clone and install the Perl module:
git clone https://github.com/lausser/perl-sapnwrfc.git cd perl-sapnwrfc perl Makefile.PL --source /path/to/nwrfcsdk make make install - Copy the shared libraries to your OMD site’s library directory
For detailed SNC setup instructions, see our blog post: Using check_sap_health with SNC
Command Line Parameters
Connection Parameters
-
--hostname / --ashost The hostname or IP address of the SAP application server.
-
--sysnr The SAP system number (instance number).
-
--username The SAP user for RFC connection.
-
--password Password of the SAP user.
-
--client The SAP client number. Default: 001
-
--lang The language for connection. Default: EN
-
--mshost The message server hostname (for load balancing).
-
--msserv The message server port.
-
--r3name The SAP system ID (SID) when connecting via message server.
-
--saprouter SAP Router connection string (e.g.,
/H/router.example.com). Routes the connection through an SAP Router, which can be combined with SNC for encrypted communication through a single gateway.
Filtering Parameters
-
--name Filter for specific objects (usage depends on mode).
-
--name2 Additional filter parameter for narrowing results.
-
--name3 Third level filter parameter.
-
--regexp Treat name filters as regular expressions.
Operational Parameters
-
--mode Specifies what the plugin should check. See “Modes” section below for available values.
-
--lookback Time window in seconds for historical data analysis.
-
--separator Separator character for MTE (Monitoring Tree Element) paths. Default: ->
-
--mtelong Output complete MTE paths in plugin output.
Threshold Parameters
-
--warning / --warningx Warning threshold. Use --warningx to override SAP’s default thresholds.
-
--critical / --criticalx Critical threshold. Use --criticalx to override SAP’s default thresholds.
Output Parameters
- --report <short|long|html> Output format for the check results.
SNC (Secure Network Communication) Parameters
-
--snc Enable SNC protocol for encrypted communication. Sets environment variable
SNC_MODE=1. -
--secudir Directory containing the
SAPSNCS.psefile (Personal Security Environment). -
--snc-lib Path to the
libsapcrypto.solibrary. If not specified, the plugin searchesLD_LIBRARY_PATH. -
--snc-myname SNC name identifying the monitoring system (sets
SNC_MYNAME). -
--snc-partnername Distinguished Name (DN) of the SAP system’s certificate (sets
SNC_PARTNERNAME). -
--snc-qop Quality of Protection level (sets
SNC_QOP). Default: 3- 1 = Authentication only
- 2 = Integrity protection
- 3 = Privacy protection (encryption)
- 8 = Use default protection
- 9 = Maximum protection
Extension Parameters
- --with-mymodules-dyn-dir Directory path for custom extension modules.
Modes
check_sap_health supports various modes for different monitoring tasks:
Connection Testing
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| connection-time | Measures how long connection establishment and login take |
CCMS Monitoring
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| list-ccms-monitor-sets | Lists all available CCMS monitor sets |
| ccms-mte-check | Checks specific CCMS Monitoring Tree Elements |
Short Dump Analysis
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| shortdumps-list | Lists all short dumps |
| shortdumps-count | Counts short dumps within a time window |
| shortdumps-recurrence | Monitors recurring short dumps |
Short Dumps Monitoring Examples
The plugin provides detailed monitoring of SAP short dumps with visual feedback in monitoring interfaces:
Recurring Short Dumps Detection:
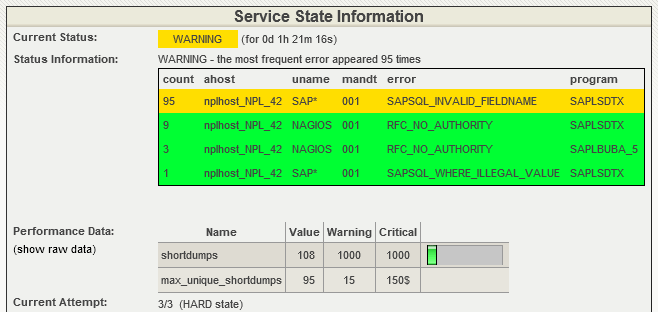
The plugin tracks short dump patterns and alerts on recurring issues
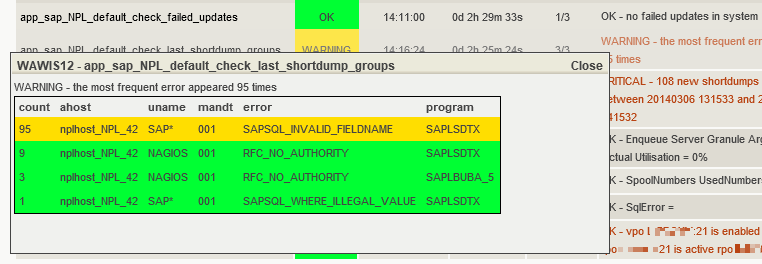
Detailed popup showing short dump analysis and history
Short Dumps Count:

Count-based monitoring with configurable thresholds and time windows
Job Monitoring
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| list-jobs | Lists background jobs |
| failed-jobs | Checks for failed background jobs |
| exceeded-failed-jobs | Monitors jobs that exceeded their expected runtime |
Process Monitoring
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| list-processes | Lists SAP work processes |
| count-processes | Counts work processes by type |
IDoc Monitoring
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| list-idocs | Lists IDocs |
| failed-idocs | Checks for failed IDocs |
System Analysis
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| failed-updates | Checks for failed update requests |
| workload-overview | Analyzes system workload statistics |
Extensions
check_sap_health can be extended with custom functionality through Perl modules. This allows you to monitor business-specific metrics and processes.
Creating Custom Modules
- Create a Perl module following the naming convention:
CheckSapHealth*.pm - Place the module in
$OMD_SITE/etc/check_sap_health/ - The module must inherit from
Classes::SAP::Netweaver::Item - Use the
--with-mymodules-dyn-dirparameter to specify the module directory
Example Module Structure
package CheckSapHealthCustom;
use strict;
use base qw(Classes::SAP::Netweaver::Item);
sub init {
my ($self) = @_;
# Your initialization code
}
sub nagios {
my ($self) = @_;
# Your check logic
# Set $self->{nagios_level} and $self->{nagios_message}
}
1;
Examples
Basic Connection Test
check_sap_health \
--hostname sap.example.com \
--sysnr 00 \
--username nagios \
--password secret \
--client 100 \
--mode connection-time
CCMS Monitoring with Filters
check_sap_health \
--hostname sap.example.com \
--sysnr 00 \
--username nagios \
--password secret \
--client 100 \
--mode ccms-mte-check \
--name "SAP CCMS Monitor Templates" \
--name2 "Dialog Overview" \
--name3 "ResponseTime" \
--mtelong
Monitoring via Message Server (Load Balancing)
check_sap_health \
--mshost sap-msg.example.com \
--msserv 3600 \
--r3name PRD \
--username nagios \
--password secret \
--client 100 \
--mode workload-overview
Secure Connection with SNC
check_sap_health \
--hostname sap.example.com \
--sysnr 00 \
--username nagios \
--password secret \
--client 100 \
--mode ccms-mte-check \
--name "Dialog" \
--snc \
--secudir /omd/sites/mysite/etc/check_sap_health/sec \
--snc-partnername "p:CN=SAP_PRD,O=Company,C=DE"
Using SAP Router
check_sap_health \
--saprouter "/H/router.example.com" \
--hostname sap.example.com \
--sysnr 00 \
--username nagios \
--password secret \
--client 100 \
--mode connection-time
Threshold Syntax
Thresholds follow the Nagios plugin development guidelines:
10means “Alarm if > 10”10:means “Alarm if < 10”10:20means “Alarm if < 10 or > 20”@10:20means “Alarm if between 10 and 20”
Directory Layout in OMD
| Path | Description |
|---|---|
<site>/lib/nagios/plugins/ |
Binary directory (provided by OMD Release) |
<site>/local/lib/ |
Library directory for SDK files |
<site>/etc/check_sap_health/ |
Configuration and extension modules |
SAP Permissions
The SAP user used for monitoring requires specific authorizations. The minimal authorization profile should include:
- RFC function groups for CCMS access
- Read access to background job tables
- Access to system monitoring functions
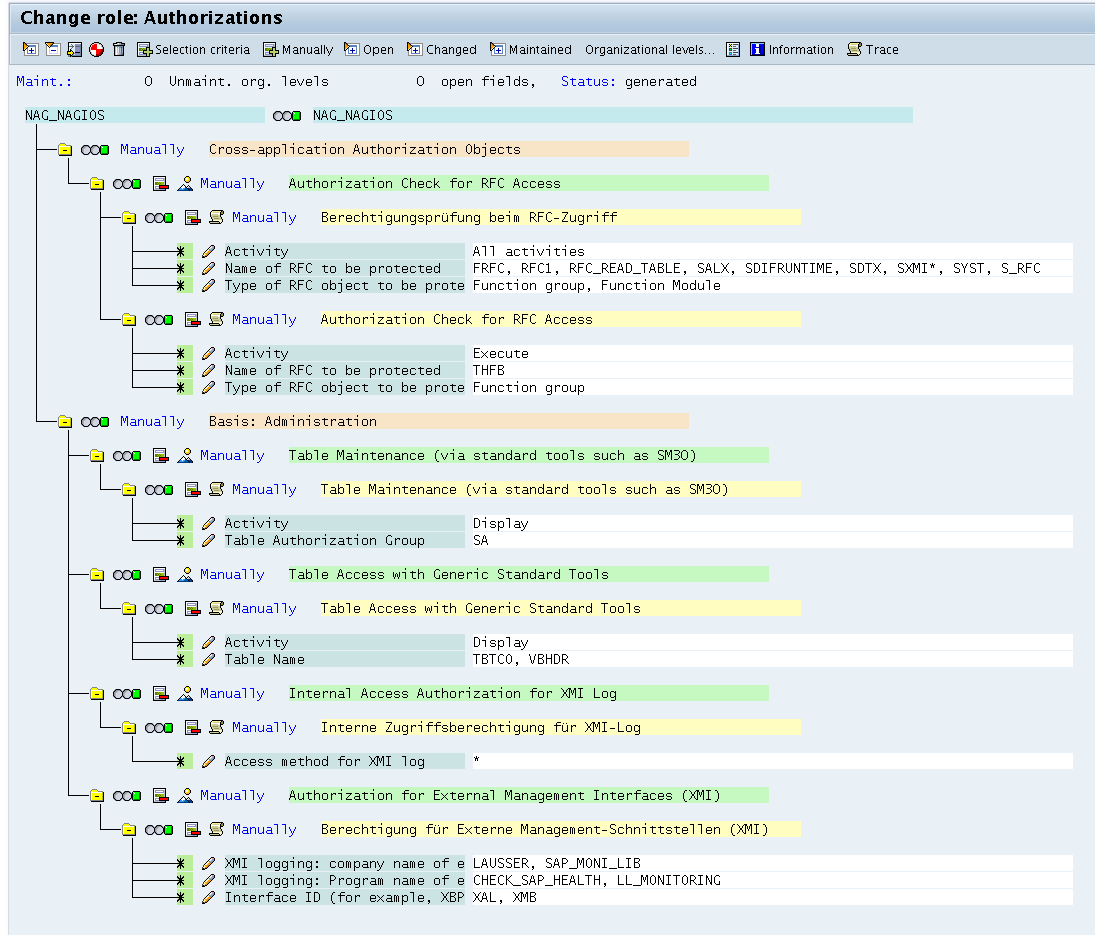
Required SAP authorizations and access levels for monitoring operations
Consult your SAP Basis team to create an appropriate monitoring user with restricted permissions. The diagram above shows the complete authorization hierarchy needed for full plugin functionality.
Resources
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/lausser/check_sap_health
- Changelog: https://github.com/lausser/check_sap_health/blob/master/ChangeLog
- Perl Module (sapnwrfc): https://github.com/lausser/perl-sapnwrfc
Author & License
Author: Gerhard Laußer, ConSol Labs
License: GNU General Public License
See Also
- Using check_sap_health with SNC - Detailed guide for setting up SNC
- OMD Packages - Overview of included monitoring plugins